Temperature control is a critical aspect of storing and transporting sensitive medical products. As pharmaceutical research advances and new drugs emerge, the importance of maintaining optimal conditions throughout the supply chain increases. Pharmaceutical freezers play a pivotal role in safeguarding the integrity of vaccines, biologics, and other temperature-sensitive medications.
Why temperature stability matters
Many medications, including vaccines, insulin, and certain cancer treatments, are highly sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Exposure to improper storage conditions can compromise their efficacy or render them completely ineffective. Even minor deviations in temperature can result in chemical changes that are invisible to the naked eye but have significant consequences for patient safety and treatment outcomes.
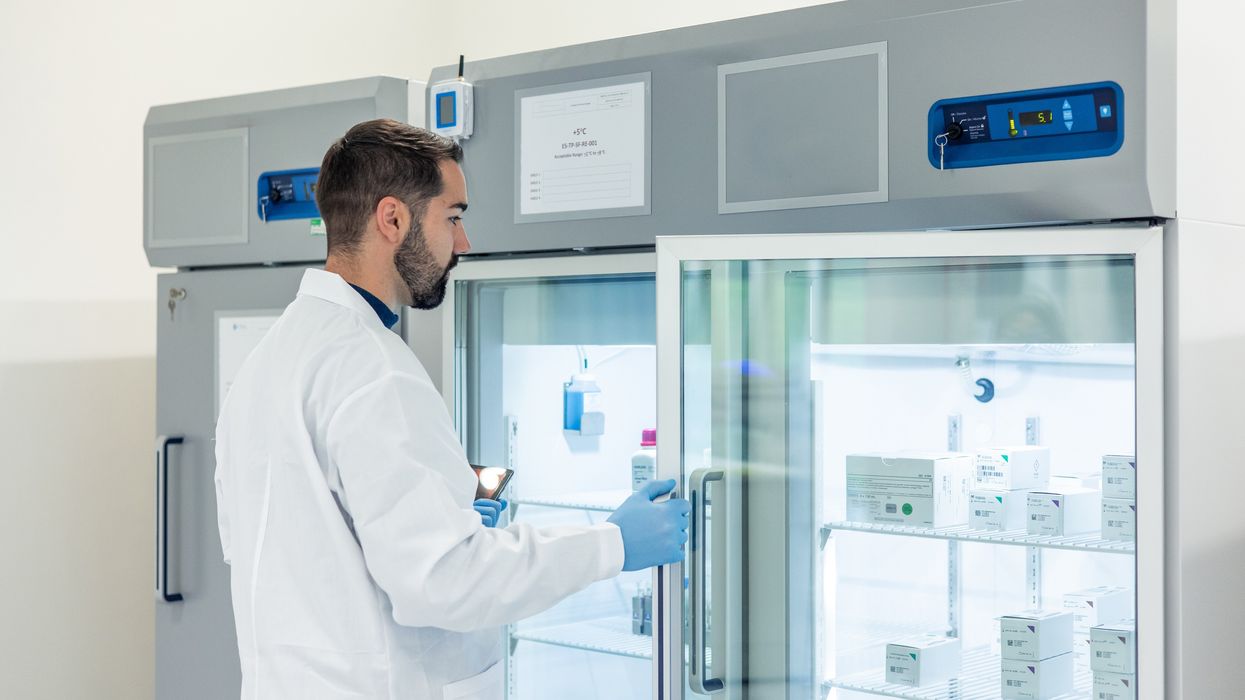
Pharmaceutical freezers are specifically designed to maintain strict temperature ranges, often at sub-zero levels, to ensure that products remain stable from the moment they are manufactured until they reach the patient. Unlike standard commercial freezers, these units must adhere to rigorous standards set by regulatory bodies such as the FDA and EMA.
The technology behind pharmaceutical freezers
Modern pharmaceutical freezers incorporate advanced technologies to ensure continuous temperature monitoring and consistent performance. Features such as digital temperature controls, alarm systems, backup power supplies, and data logging are standard in these freezers. This technology allows for detailed records of storage conditions, which are essential for regulatory compliance and quality assurance.
Remote monitoring capabilities are increasingly common, enabling pharmaceutical companies and healthcare providers to track freezer performance in real time. If a temperature deviation occurs, designated personnel receive immediate alerts, allowing them to take corrective action before any damage occurs. This level of oversight is crucial in environments where even the smallest lapse can have far-reaching consequences.
The cold chain: A delicate balance
The concept of the “cold chain” refers to the network of temperature-controlled environments required to move pharmaceutical products from manufacturing facilities to end users. Each link in this chain must be carefully managed to prevent temperature excursions that could compromise product quality. Pharmaceutical freezers are a cornerstone of this system, ensuring that drugs and vaccines remain potent and safe throughout their journey.
In addition to stationary freezers used in laboratories and pharmacies, portable and transportable units are essential for moving products between locations. These specialized freezers are designed to withstand the rigors of transportation, including vibration, variable climates, and power interruptions. Their reliability is vital for reaching remote areas or responding to emergencies where rapid deployment of medications is necessary.
Evolving needs in the pharmaceutical sector
As the pharmaceutical sector evolves, so do the requirements for storage solutions. The rise of personalized medicine and biologics has increased the demand for ultra-low temperature storage. Some therapies require storage at temperatures as low as -80°C, far beyond the capabilities of traditional refrigeration systems. Pharmaceutical freezers that meet these demands are now a standard fixture in research institutions, hospitals, and distribution centers worldwide.
The shift towards more stringent regulations and quality standards has also influenced the development of pharmaceutical freezers. Manufacturers must now demonstrate that their equipment can consistently maintain required temperatures under a variety of conditions. Validation and regular maintenance are essential to ensure ongoing reliability and compliance.
Challenges and future directions
Despite technological advancements, the sector faces ongoing challenges. Energy consumption remains a concern, as ultra-low temperature freezers require significant power to operate. Efforts to develop more energy-efficient models are underway, with manufacturers exploring alternative cooling technologies and improved insulation materials.
Another challenge is the integration of freezers with digital supply chain management systems. As data becomes increasingly central to pharmaceutical logistics, the ability to seamlessly track and analyze storage conditions is becoming a competitive advantage. Freezers that offer connectivity and interoperability with broader IT systems are likely to become more prevalent.
Looking ahead: The continued importance of reliable freezing solutions
The ongoing development of new therapies, particularly those based on biological materials, will keep pharmaceutical freezers at the forefront of medical logistics. Their role extends beyond storage; they are a vital link in ensuring that patients receive safe, effective treatments. As expectations for quality and safety continue to rise, the need for dependable, high-performance freezing solutions will only intensify.
In summary, the integration of advanced pharmaceutical freezers into the medical supply chain is not just a matter of convenience—it is a necessity for protecting patient health and supporting innovation in medicine. Their presence behind the scenes is indispensable, and their impact will only grow as new challenges and opportunities emerge in the pharmaceutical landscape.